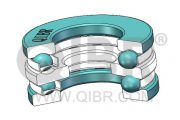
The thrust bearing is a rotary bearing that rotates between components to reduce friction and is designed to support axial loads (mainly used in low-speed applications). Its function is to prevent the shaft from drifting in the axial direction and transmit the thrust load applied to the shaft.
Thrust bearings are usually mounted on a protruding thrust ring around the shaft. The thrust ring allows the axial load to be transmitted from the shaft to the bearing. Thrust bearings are usually used in pairs on each side of the thrust ring.
Thrust ball bearings are commonly used in aerospace, chemical and utility industries, and thrust bearings are also commonly used in automotive and marine applications.